Product Highlight: How to Build Organisational Hierarchies in Falcony | Observe
Organisations come in as many shapes and sizes as there are companies and industries. Even though many employees aren’t fond of them, the fast paced and hectic world requires companies to have more organised structures in their operations. This is one way that helps the companies to adapt quicker to different environments and changes in the market.
Some of the most common organisational hierarchies are:
- The Matrix
- The Hierarchical Structure
- The Horizontal / Flat Structure
- Line Organisational Structure
- The Network Structure
- The Divisional Structure
Creating your organisation with places and tags
Places and tags
When an organisation is added to Falcony the ideal case is that Falcony | Observe can mirror the organisational structure and hierarchy of it, so that it matches the real world organisational hierarchy as closely as possible. To do that we have created the tags functionality so that you can easily structure different parts of the hierarchy.
Tags are factors about your places or locations that let you group them into segments. They can be defined to be anything from retail brands and geographical territories to manufacturing business units, field service customer segments, and employees’ roles in the organisation.
The tags are, furthermore, also taking into consideration that organisations can differ a lot by how different departments, functions and divisions are defined so it is important that Falcony can adapt to these. This is especially important as the tool is being used in many industries, In retail the lowest organisational units are often stores, or markets. Whereas in hospitality it is restaurants, hotels and so on.
However not all businesses have physical sites. Some would have cost centres, projects or/and delivery routes that employees and departments would belong to.
What makes things more complex is when employees might belong to multiple targets and locations.
This is where the tag management in Falcony comes in.
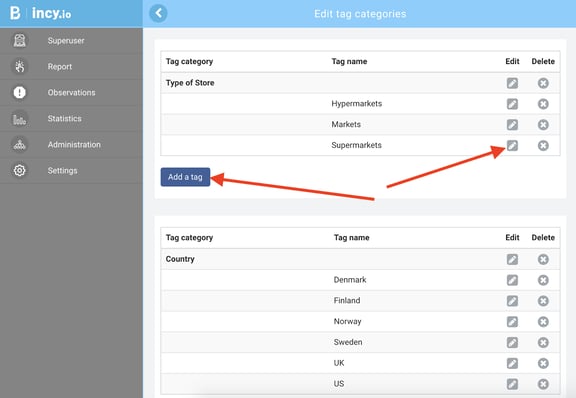
With the tag management of places and locations, you manage the hierarchy and user rights of users in your organisation in a nuanced way with the tool. As an administrator you can add as many tag categories, with as many tags as you would like.
Most SaaS solutions include predefined roles such as Admin, Moderator, Editor, Viewer, etc. These roles give specific rights per user which can be customised under each user. But then on the other hand, not a lot of SaaS solutions are used by thousands or tens of thousands of users for multiple different use cases, where user right changes need to be quickly carried out to multiple users at once. That is why we have built “Roles” that are fully customisable to different organisational nuances and structures.
Roles
The “Roles” function is great for building the normal superior-subordinate relationship structure that can differentiate a lot by organisations. It also helps to take into account more siloed responsibilities, such as Safety that should see everything related to safety and nothing else, or Quality that should be notified of all quality related workflows, and so on.The “Roles” function can be used to determine and limit user rights by:
- What a user can report
- What a user can see
- What a user can edit
- What a user can be assigned to
- What a user is assigned to by default
- Whether a user can see other participants or not
- Whether a user can assign observations or not
- What a user will be notified about by default
Defining user rights with tags and roles
When user rights are defined with customisable tags, custom roles and places the result is a powerfully mapped hierarchy of what different organisations can look like regardless of size, industry or number of use cases.
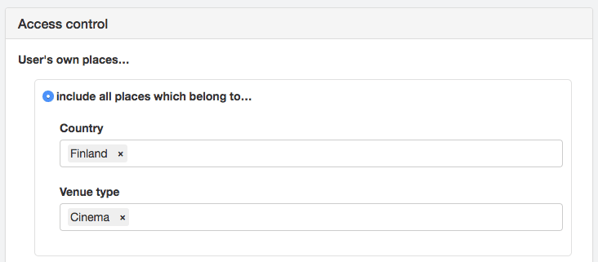
Once the role is set, you can set up existing users for specific roles, and invite new users under that role. When doing this, just choose which places or tags (can be one or multiple) that specific users belong to. All users and their user rights are managed from the “Role” specifications.
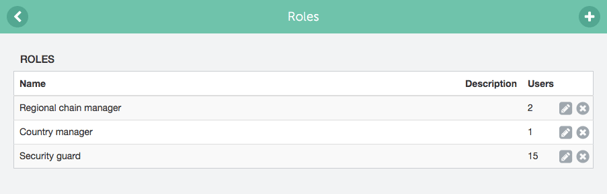
This takes into account when employees change departments or are promoted, so all you need to do is to update the role and the places or them in the tool.
Integrations to HR-, ERP- and CRM-systems
The bigger the organisation the more changes there are both in terms of places (sites, projects, etc.) and especially users. Also taking into consideration that the time of the admin user is not the least expensive, it often makes sense to integrate the “Roles” and user rights from the organisation’s HR system (e.g. Workday, SAP, or similar), and take “Places” and “Tags” from an ERP or CRM system to incy.io. Time saved here is time spent more effectively and productively elsewhere, such as coming up with more use cases with Falcony.
Example Tags And Roles By Industry
Retail:
Places: Stores.
Tags: Chains, brands, companies, geographical positioning such as countries and areas.
Roles: Employees, Store Managers, Area Managers, Chain Managers, Country Managers, Visual Merchandising Team, Security Team, OHS Representatives, and Environmental Managers, Executives, just to name a few.
Manufacturing:
Places: Cost Centres or Manufacturing lines.
Tags: Product categories, Market areas, Countries, Divisions, Business units and Functions.
Roles applied to users: Employees, Production Managers, Logistics Managers, Safety Managers, Functional Directors, Quality Manager, Business Line Managers, OHS Representatives, Environmental Managers and Executives.
Field Operations (Maintenance & Cleaning):
Places: Projects or Customer’s sites.
Tags: Customers, Customer Segments, Areas, Business Units, Countries, etc.
Roles applied to users: Cleaners, Maintenance workers, Foremen, Account Managers and Sales Directors.
Final thoughts
Falcony | Observe is so much more than just an incident reporting tool. You can use it to create complex forms and workflows and track performance of different areas of your organisation. To make sure that your business processes are managed effectively use the “Tags”, “Places” and “Roles” functions in the tool. Mapping organisation as it works in the real world helps admin users with the user adoption of the software and the management of changes that eventually will happen.
For more information on how you can set this up for your organisation, see this help centre article on Tag Management. See also this help centre article on Roles in incy.io to learn more about how to set up different user rights and custom roles for your organisation.
If you don’t currently have incy.io in use, and would like to, contact our support team, or sign-up for a free trial to get started.
We are building the world's first operational involvement platform. Our mission is to make the process of finding, sharing, fixing and learning from issues and observations as easy as thinking about them and as rewarding as being remembered for them.
By doing this, we are making work more meaningful for all parties involved.
More information at falcony.io.

Related posts
Product Highlight: Signature questions in Falcony | Observe
Since the inception of Falcony | Observe, we envisioned making reporting and managing all types of...
How to promote Blameless Reporting with organisational culture
Issue reporting and incident reporting tend to be areas of difficulty for most businesses. Many...
A book summary of Drift into failure by Sidney Dekker.
"Drift into Failure" is a book by Sidney Dekker that examines the ways in which complex systems can...



